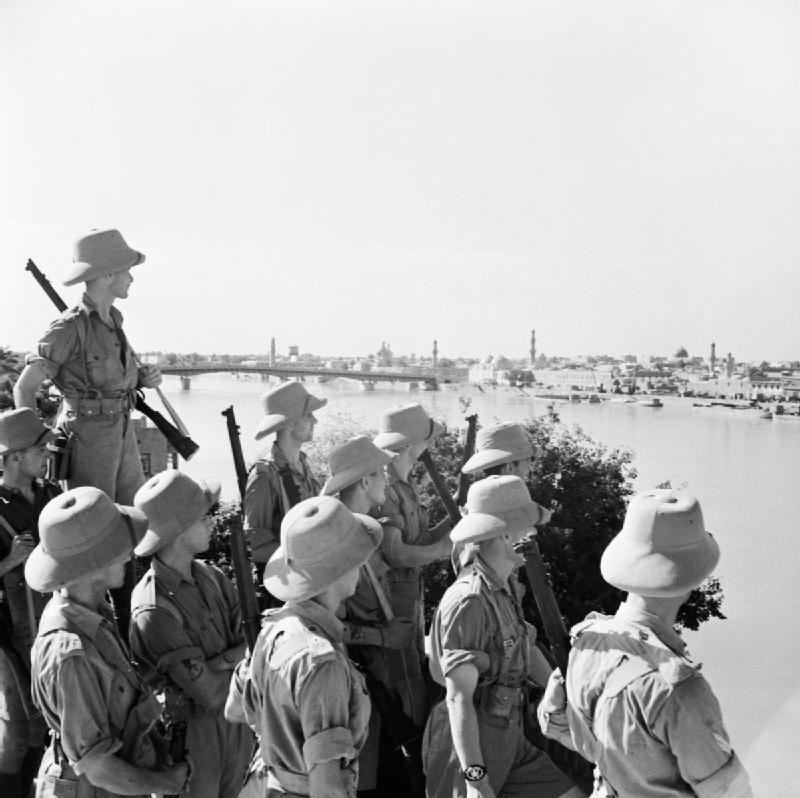
The Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre was a major theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre saw interconnected naval, land, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe. The fighting in this theatre lasted from 10 June 1940, when Italy entered the war on the side of Germany, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis forces in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Greece – where British troops had been dispatched to aid the Greek government – during the early stages of the Greek Civil War.
The British referred to this theatre as the Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre (so called due to the location of the fighting and the name of Middle East Command), the Americans called it the Mediterranean Theater of War and the German informal official history of the fighting is The Mediterranean, South-East Europe, and North Africa 1939–1941 (1995). Regardless of the size of the theatre, the various campaigns were not seen as neatly separated areas of operations but part of a vast theatre of war.
Fascist Italy aimed to carve out a new Roman Empire, while British forces aimed initially to retain the status quo. Italy invaded Greece, and not until the introduction of German forces were Greece and Yugoslavia overrun. Allied and Axis forces engaged in back and forth fighting across North Africa, with Axis interference in the Middle East causing fighting to spread there. With confidence high from early gains, German forces planned elaborate attacks to be launched to capture the Middle East and then to possibly attack the southern border of the Soviet Union. In three years of fighting, Axis forces were defeated in North Africa and their interference in the Middle East was halted. The anti-Axis coalition then commenced the Allied invasion of Italy, resulting in the Italians deposing Mussolini and joining the Allies. A prolonged battle for Italy took place between Allied and Axis forces. As the strategic situation changed in south-east Europe, British troops returned to Greece.
The theatre of war had the longest duration of the Second World War, resulted in the destruction of the Italian Empire and severely undermined the strategic position of Germany, resulting in German divisions being deployed to Africa and Italy and total German losses (including those captured upon final surrender) being over two million.[c] Italian losses amounted to around 177,000 men with a further several hundred thousand captured during the process of the various campaigns. British losses amount to over 300,000 men killed, wounded, or captured, and total American losses in the region amounted to 130,000.