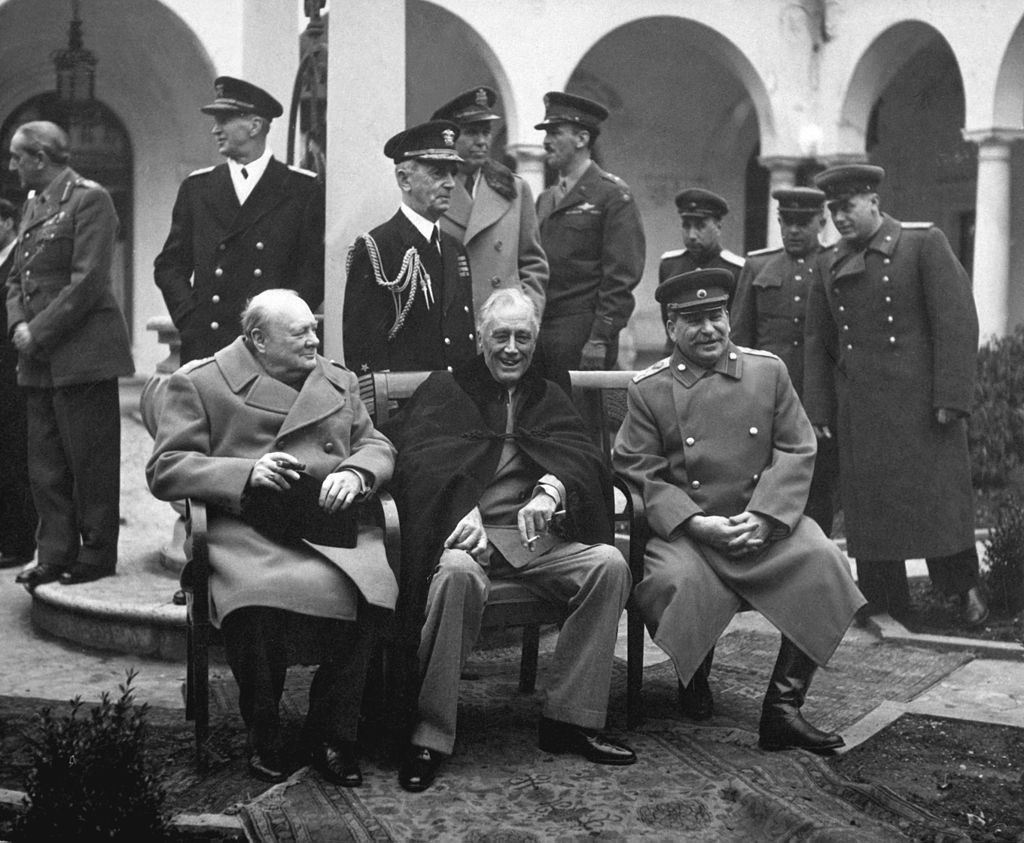
Germany and the Soviet Union were sworn enemies, but following the Munich Agreement, which effectively handed over Czechoslovakia (a French and Soviet ally, and the only remaining presidential democracy in Central Europe) to Germany, political realities allowed the Soviet Union to sign a non-aggression pact (the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact) including a secret clause partitioning Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia and Finland between the two spheres of influence.
Full-scale war in Europe began at dawn on 1 September 1939, when Germany used so-called Blitzkrieg tactics and military strength to invade Poland, to which both the United Kingdom and France had pledged protection and independence guarantees. On 3 September 1939, Britain and France declared war on Germany, and other allies soon followed. The British Expeditionary Force was sent to France; however, neither French nor British troops gave any significant assistance to the Poles during the entire invasion, and the German–French border, excepting the Saar Offensive, remained mostly calm. This period of the war is commonly known as the Phoney War.
On 17 September the Soviet forces joined the invasion of Poland, although remaining neutral with respect to Western powers. The Polish government evacuated the country for Romania. Poland fell within five weeks, with its last large operational units surrendering on 6 October after the Battle of Kock. As the Polish September Campaign ended, Hitler offered Britain and France peace on the basis of recognition of German European continental dominance. On 12 October the United Kingdom formally refused.
Despite the quick campaign in the east, along the Franco-German frontier the war settled into a quiet period. This relatively non-confrontational and mostly non-fighting period between the major powers lasted until Germany launched an invasion on 10 May 1940.