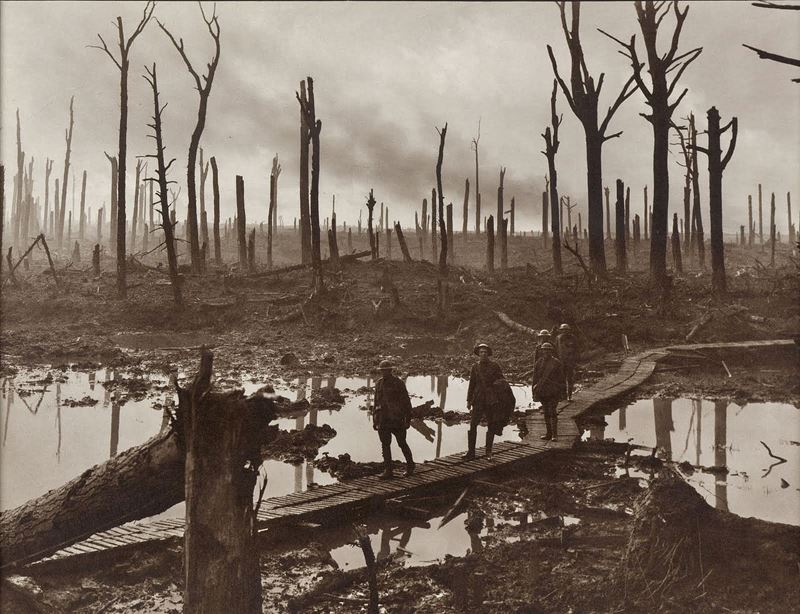
The Third Battle of Ypres (German: Dritte Flandernschlacht; French: Troisième Bataille des Flandres; Dutch: Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (/ˈpæʃəndeɪl/), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire.[a] The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, 5 mi (8.0 km) from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere (Koekelare).
Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport (Nieuwpoort), combined with an amphibious landing (Operation Hush), were to have reached Bruges and then the Dutch frontier. Although a general withdrawal had seemed inevitable in early October, the Germans were able to avoid one due to the resistance of the 4th Army, unusually wet weather in August, the beginning of the autumn rains in October and the diversion of British and French resources to Italy. The campaign ended in November, when the Canadian Corps captured Passchendaele, apart from local attacks in December and early in the new year. The Battle of the Lys (Fourth Battle of Ypres) and the Fifth Battle of Ypres of 1918, were fought before the Allies occupied the Belgian coast and reached the Dutch frontier.