
Operation Vulture
Table of Contents Operation Vulture was the name of a US operation planned to rescue French troops from a B-29 raid into the Philippines during

Table of Contents Operation Vulture was the name of a US operation planned to rescue French troops from a B-29 raid into the Philippines during
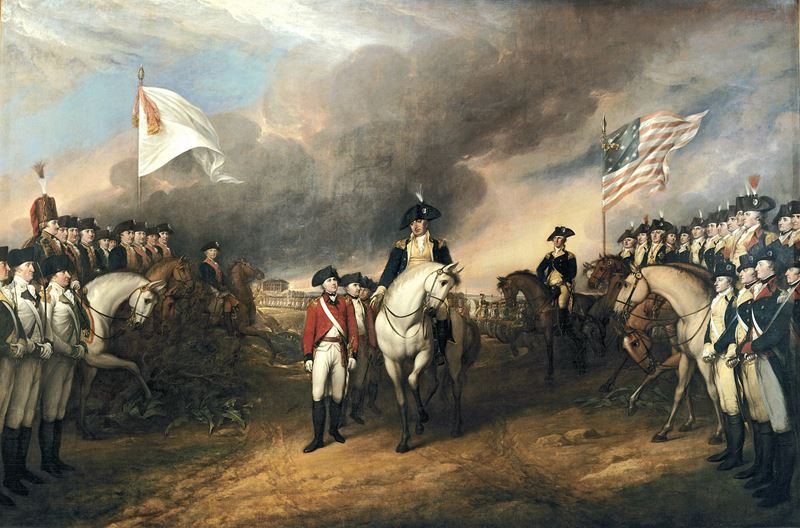

French involvement in the American Revolutionary War of 1775–1783 began in 1776[1] when the Kingdom of France secretly shipped supplies to the Continental Army of

In the United States, each state has its own written constitution. They are much longer than the United States Constitution, which only contains 4,543 words.
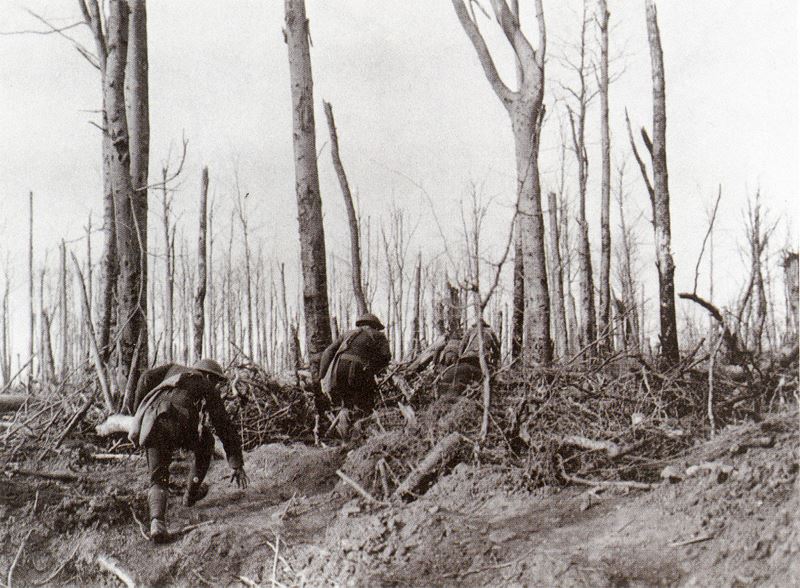

The Meuse–Argonne offensive (also known as the Meuse River–Argonne Forest offensive,[6] the Battles of the Meuse–Argonne, and the Meuse–Argonne campaign) was a major part of
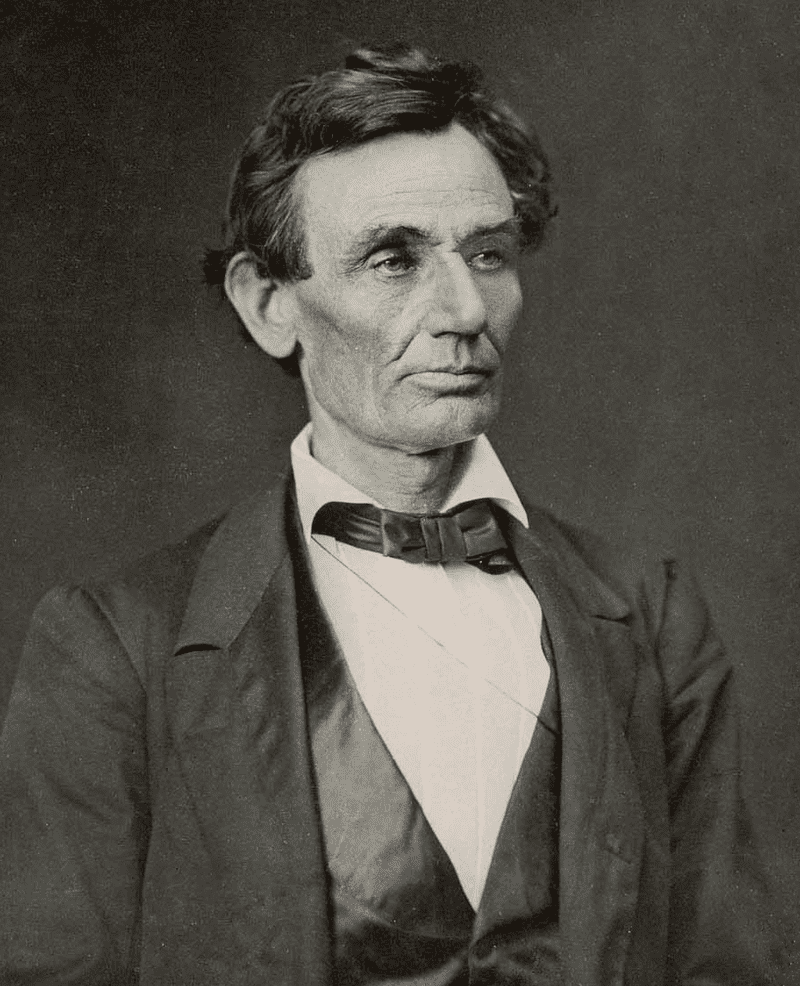
The election of Abraham Lincoln in November 1860 was the final trigger for secession.[109] Southern leaders feared that Lincoln would stop the expansion of slavery
Throughout history, humanity has been shaped by the crucible of warfare. Historical battles serve as milestones, representing the clash of empires, the rise and fall

The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allied offensives which ended the First World War. Beginning with

The Strategic Hamlet Program (SHP; Vietnamese: Ấp Chiến lược ) was a plan by the government of South Vietnam in conjunction with the US government