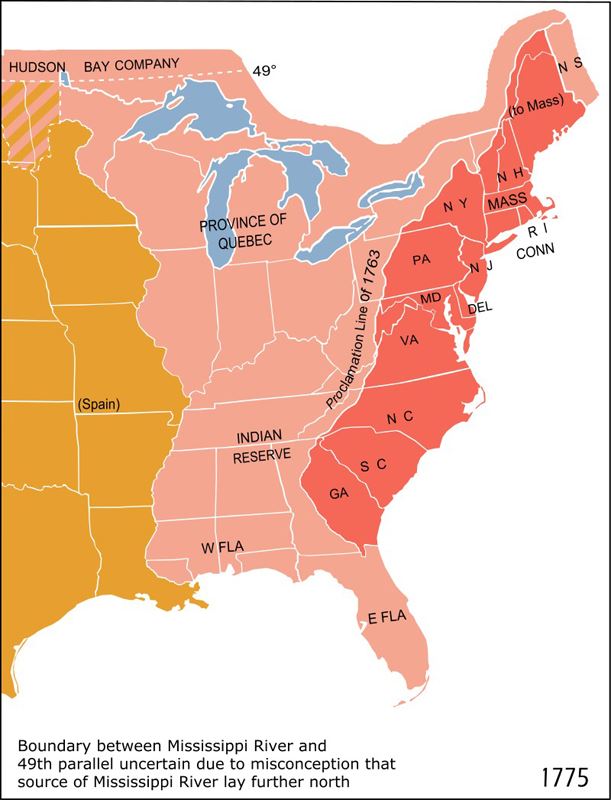
The governments of the Thirteen Colonies of British America developed in the 17th and 18th centuries under the influence of the British constitution. After the Thirteen Colonies had become the United States, the experience under colonial rule would inform and shape the new state constitutions and, ultimately, the United States Constitution.[1]
The executive branch was led by a governor, and the legislative branch was divided into two houses, a governor’s council and a representative assembly. In royal colonies, the governor and the council were appointed by the British government. In proprietary colonies, these officials were appointed by proprietors, and they were elected in charter colonies. In every colony, the assembly was elected by property owners.
In domestic matters, the colonies were largely self-governing; however, the British government did exercise veto power over colonial legislation. Diplomatic affairs were handled by the British government, as were trade policies and wars with foreign powers (wars with Native Americans were generally handled by colonial governments).[2][page needed]
The American Revolution was a dispute over the British Parliament’s right to enact domestic legislation for the American colonies. The British government’s position was that Parliament’s authority was unlimited, while the American position was that colonial legislatures were coequal with Parliament and outside of its jurisdiction. As the Revolution progressed, the colonial governments were replaced by temporary provincial congresses and ultimately by republican constitutions.