Table of Contents
“Border States” refers to the slave states that surrounded the free states that made up the Union. When it came to winning the American Civil War, these states were important for both the Union and the Confederacy. Both the Union and the Confederacy relied on the Border States, but the latter especially so that they could keep their slave populations under control. Moreover, the resources, such as food and animals, that the Border States had were crucial.
The Border States were crucial to the Union’s success during the Civil War. This group of people was seen by the Union as a potential source of labor and supplies. They played an important role in the Confederacy’s plan to maintain power over its slave population. Many people in the Border States fled to Union territory as a result of the conflict.
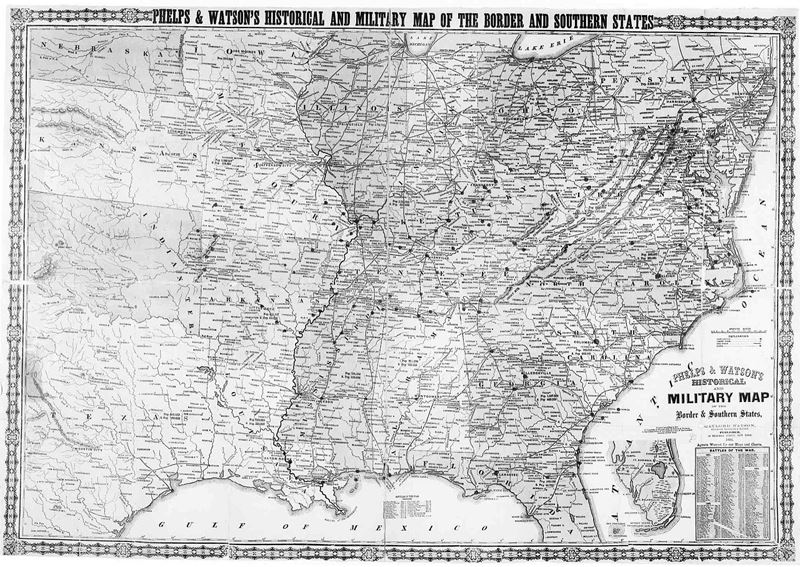
The Border States During the American Civil War
During the time of the American Civil War, the states of West Virginia, Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, and Delaware were considered to be the Border States.
Delaware border state: Due to the fact that Delaware was one of the northernmost border states and featured vital port cities as well as rivers, the state was strategically significant for the Union. Despite the small number of slaves who were actually held by Delaware residents, the state was historically a slave state.
Maryland border state: Because major railways passed through Maryland, the state had an important role as a supply route for the northern states. Instead of maintaining a neutral stance, Maryland took an aggressive stance in favor of the Union and abolished slavery in 1864.
Missouri border state: Both the Union and Confederate armies made attempts to lay claim to Missouri as their own territory during the Civil War. Both the Union and the Confederacy created administrations in this state, which resulted in some of the worst combat that occurred in the Border states area.
Kentucky border state: Politicians in Kentucky were among the most vocal in support of compromise and negotiation between the North and South. So, although Kentucky was a slave state whose beliefs aligned firmly with the Confederacy, they decided to stay neutral in the war and remain a part of the U.S.
Once the Confederacy started advancing its military into Kentucky, its neutrality was threatened. They reached out to Lincoln for support. Union troops were sent to repel the Confederate invaders, strengthening ties between Kentucky and the Union.
West Virginia border state: The newly founded state of West Virginia became the 35th member of the United States of America in the year 1863. Slavery was not illegal in these states, despite the fact that they remained part of the Union. The Union was able to maintain key communication and supply lines by maintaining control of West Virginia, which allowed them to hang on to the Baltimore and Ohio railway lines.
These states continued to be part of the Union while having a slave-based economy. Obtaining the support of these states was one of the foremost aims of the Union in an attempt to prevent their accession to the Confederacy. The recruitment of individuals from these states into the Confederacy was the primary objective of the Confederate military. A significant contribution to the American Civil War was made by the Border States.
The Significance of Border States to the American Civil War
During the course of the American Civil War, the Border States were of the utmost significance to the Union cause. They not only served as a physical barrier between the Confederacy and the rest of the nation, but the economy of these states was also very important to the Northern states. In addition, the Border States were home to a sizable number of African Americans, who would go on to play an important part in the operations of the Union army.
The Border States played an extremely essential role in ensuring the Union’s victory in the American Civil War. While their economies contributed much-needed resources to the Union war effort, the physical position of these states functioned as a barrier between the Confederacy and the Northern states.
In addition, African Americans who lived in states that were considered to be on the Union’s border played an essential part in supporting and fighting for the Union cause. It is very doubtful that the Union would have won the Civil War without the assistance of these crucial states.
During American Civil War Union's Border States Policy
The objective of the Union’s policy for the border states was to continue to exercise authority over the region and to stop the Confederates from establishing a foothold there. The Confederates were able to be kept at bay in the border states due to the strong presence that the Union maintained there. The border states were also used by the Union as a base of operations from which to launch raids into the Confederate states. The approach used by the Union was effective in maintaining control of the border states and preventing the Confederacy from establishing a foothold in those areas.
The border strategy used by the Confederates
The Confederacy had a dual objective when it came to their border strategy: first, they wanted to ensure the safety of their own borders, and second, they aimed to gain an edge by using the fact that the Union had to protect a far greater territory. In order to accomplish the first objective, the Confederacy constructed a string of forts along its borders, the most notable of which was Fort Sumter in South Carolina.
The second objective was more difficult to accomplish, but the Confederates were able to achieve some level of success in recruiting inhabitants of border states to support their cause. Confederate armies, for instance, were able to recruit some men from the states of Kentucky and Missouri since they held portions of both states at the time.
To Win the War in the Border States: The Union's Strategy
Keeping the Mississippi in Union control was the key to victory in the border states during the American civil war. Whoever controlled the river would have a significant advantage in the area since it was vital to the flow of trade and communication. Border states were an important economic and agricultural resource for the Union; thus, their loss would have been devastating. In addition, many African Americans living in border states might serve as soldiers in the Union.
At the outset of their campaign, the Union army took control of strategic cities in the border states along the Mississippi River. Cities like Memphis, Vicksburg, and New Orleans, Louisiana, were featured. The Union navy also laid a blockade throughout the southern coast, making it impossible for Confederate ships to enter or leave any southern ports. Furthermore, the Union army launched incursions into Confederate territory to cut off supply lines and communications.
The Union’s plan to keep the Confederacy from capturing the border states worked. There were expenses associated with this, however. It was in the border states that the Union troops suffered the most fatalities. Furthermore, the war’s effect on the economies of both sides was severe. As a result, the Border States have been left with a depleted infrastructure and a lack of functioning enterprises. They were rebuilding the area after it took a long time.
Period of Reconstruction and the Border States
During the American Civil War, the Border States played a crucial role in the Union’s eventual triumph. They were important for both sides: the Union as a strategic barrier and the Confederacy as a launching pad for military expeditions into the North. When it came to racial relations and economic growth in the aftermath of the war, the Border States were held up as national role models.
Numerous key American Civil War engagements occurred in the Border States. Confederate General Robert E. Lee’s drive into Maryland was halted in 1862 when the Union troops gained a decisive victory at the Battle of Antietam. After a failed Confederate invasion of Pennsylvania, the year before, Union forces scored a decisive victory at Gettysburg the following year. Because of the Union’s decisive victories in these two engagements, the humiliation of also being compelled to negotiate a peace treaty with the Confederacy was spared the Union due to the Union’s decisive victories.
The Border States were used as examples of post-war racial harmony and prosperous reconstruction by the other states throughout the Reconstruction period. African Americans in these states were granted full citizenship and civil rights protections by federal law in 1865. It was a major step forward in passing legislation that guaranteed racial equality in the United States. As a result of the Reconstruction period’s increased security and prosperity, many African Americans relocated to the Border States.
Final thoughts
The border states of the United States had a particularly rough time during the Civil War. Violence, economic suffering, and political infighting marked this era. Understanding the complexity of the war via the experiences of the border states is possible due to their singular and crucial role in the fight. Stories from the border states are critical to understanding the Civil War as a whole since they represent a microcosm of the wider battle between the North and the South. When all was said and done, the Civil War was a watershed event in American history, and the border states played a significant role in that narrative.