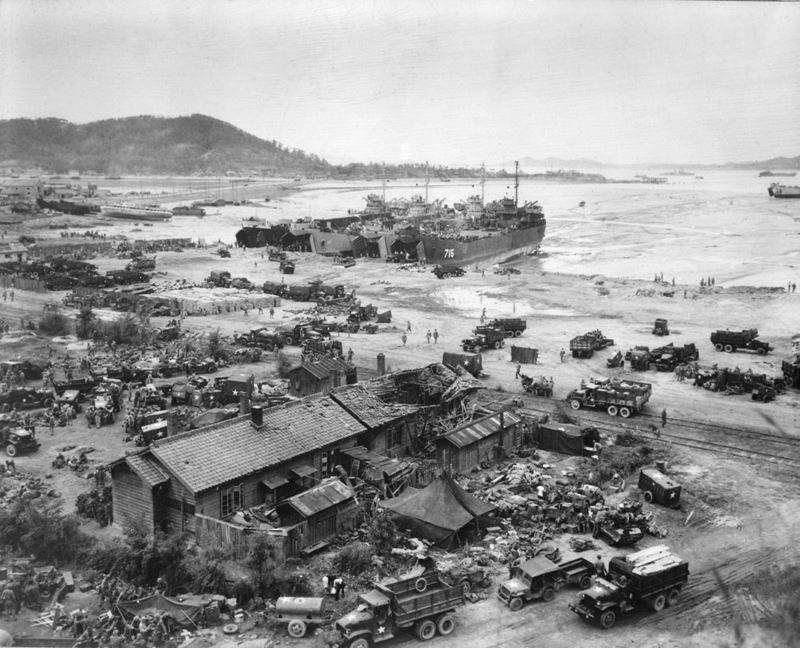
The Battle of Incheon (Korean: 인천상륙작전; Hanja: 仁川上陸作戰; RR: Incheon Sangnyuk Jakjeon), also spelled Battle of Inchon, was an amphibious invasion and a battle of the Korean War that resulted in a decisive victory and strategic reversal in favor of the United Nations Command (UN). The operation involved some 75,000 troops and 261 naval vessels and led to the recapture of the South Korean capital of Seoul two weeks later.[4] The code name for the operation was Operation Chromite.
The battle began on 15 September 1950 and ended on 19 September. Through a surprise amphibious assault far from the Pusan Perimeter that UN and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) forces were desperately defending, the largely undefended city of Incheon was secured after being bombed by UN forces. The battle ended a string of victories by the North Korean Korean People’s Army (KPA). The subsequent UN recapture of Seoul partially severed the KPA’s supply lines in South Korea.
The UN and ROK forces were commanded by General of the Army Douglas MacArthur of the United States Army. MacArthur was the driving force behind the operation, overcoming the strong misgivings of more cautious generals to a risky assault over extremely unfavorable terrain. The battle was followed by a rapid collapse of the KPA; within a month of the Incheon landing, the Americans had taken 135,000 KPA troops prisoner.